Writer Fuel: Scientists Turn Chickens Into Dinosaurs – Sort Of
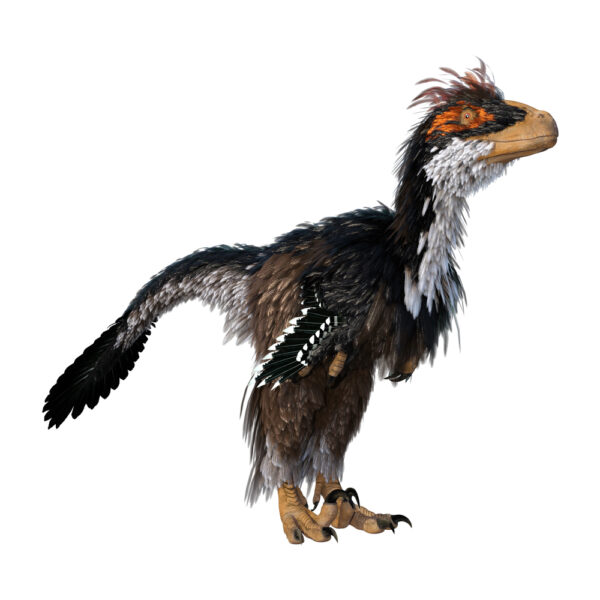
By disrupting a key gene, scientists made chicken feathers more dinosaur-like — but the results didn’t last. In a new study, researchers inhibited a gene during embryonic development to make chicken feathers more primitive, like the kind of simple tube-shaped proto-feathers that likely first emerged in the ancestors of dinosaurs in the Early Triassic 250 … Read more